How to Avoid or Remove Hemp Borer Worms from a Cannabis Harvest
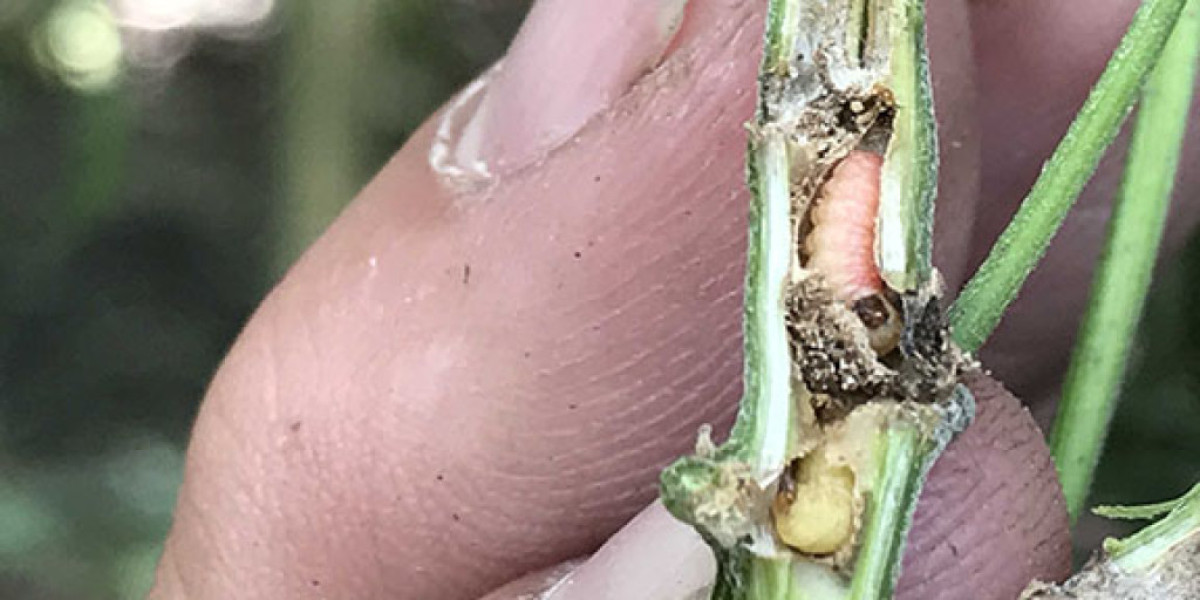
Hemp borer worms can cause significant damage to a cannabis harvest if not identified and addressed promptly. These destructive pests have the ability to tunnel into the stems of the plant, weakening its structure and potentially leading to reduced yield and overall plant health. This article will provide you with useful tips and techniques to help you avoid or remove hemp borer worms from your cannabis harvest.
1. Identify the Signs of Infestation
Early detection is crucial in preventing hemp borer worm damage. Look out for the following signs:
- Small holes or entry points in the stems
- Presence of sawdust-like frass near the entry points
- Wilting or discoloration of leaves
- Stunted growth or reduced yield
- Weak stems that easily break
- Snapping of larger stems
2. Practice Regular Inspection
Regularly inspect your cannabis plants for any signs of infestation. Check the stems, leaves, and buds carefully, paying close attention to areas near the soil. Inspecting your plants at least once a week can help you catch any early stages of infestation and prevent the worms from spreading. Be sure to inspect areas around each node for saw dust looking material. Also be on the lookout for moths flying around your plants.
3. Implement Cultural Practices
Employing certain cultural practices can help deter hemp borer worms from infesting your cannabis plants:
- Crop Rotation: Rotate your cannabis plants with different crops each growing season. This practice disrupts the reproductive cycle of the insects, making it harder for them to establish a stable population.
- Clean Surroundings: Remove any plant debris or fallen leaves near your cannabis plants regularly, as they can serve as hiding spots for the worms.
- Sanitation: Clean your gardening tools after each use to avoid unintentionally spreading any potential infestation.
- Healthy Soil: Maintain healthy soil conditions by using organic compost and beneficial soil amendments. Healthy plants are less susceptible to insect attacks.
- Spread: Be sure not to position your plants too closely together. Planting too closely together can provide a better safe haven for pests as well as quickly devastate an entire harvest rather than one or two plants.
4. Use Biological Controls
Consider implementing biological controls to combat hemp borer worms:
- Predatory Nematodes: These microscopic organisms feed on various types of pests, including hemp borer worms. Introduce them to your soil to help control the worm population.
- Parasitic Wasps: Certain species of parasitic wasps can lay their eggs inside the worms, eventually killing them. These wasps are natural enemies of many pests and can be purchased from reputable suppliers.
5. Use Organic Insecticides
If the infestation is severe and other methods have not been successful, you may consider using organic insecticides. However, it's important to note that organic insecticides can also affect beneficial insects or other organisms in the ecosystem, so be cautious when applying them.
- BT Spray: Bacillus Thuringiensis is a bacteria that will kill the worms after they have ingested it. This biological insecticide kills caterpillar-type insects, but has no effect on birds, earthworms, or beneficial insects such as honeybees and ladybugs. It can be used on fruits, vegetables, ornamentals, and shade trees.
6. Quarantine Affected Plants
If you discover infested plants, promptly separate and quarantine them from healthy ones to prevent further spreading of the pests. This can help protect your entire cannabis harvest.
7. Consult with Professionals
If you're unsure about the severity of the infestation or need additional guidance, reach out to professionals such as local agricultural extension offices or experienced growers. They can provide valuable insights specific to your region and help you develop an effective pest management plan.
By implementing these strategies, you can effectively avoid or remove hemp borer worms from your cannabis harvest, safeguarding your plants and maximizing their yield and overall health.